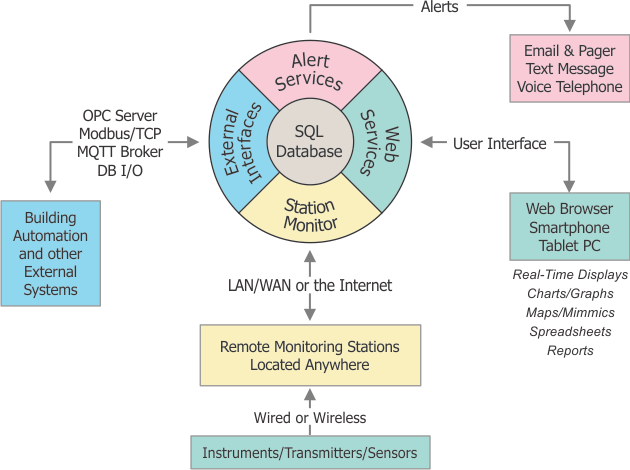
Measurement data, including values, alarm status, and a timestamp can be easily exported to other systems using OPC (SmartScan acting as the server), Modbus/TCP (SmartScan acting as a slave), and MQTT (SmartScan acting as a broker).
MQTT is a Client Server publish/subscribe messaging transport protocol. It is lightweight, open, simple, and designed so as to be easy to implement. These characteristics make it ideal for use in many situations, including constrained environments such as for communication in Machine to Machine (M2M) and Internet of Things (IoT) contexts where a small code footprint is required and/or network bandwidth is at a premium.
The protocol runs over TCP/IP, or over other network protocols that provide ordered, lossless, bi-directional connections. Its features include:
- Use of the publish/subscribe message pattern which provides one-to-many message distribution and decoupling of applications.
- A messaging transport that is agnostic to the content of the payload.
- Three qualities of service for message delivery:
- “At most once,” where messages are delivered according to the best efforts of the operating environment. Message loss can occur. This level could be used, for example, with ambient sensor data where it does not matter if an individual reading is lost as the next one will be published soon after.
- “At least once,” where messages are assured to arrive but duplicates can occur.
- “Exactly once,” where message are assured to arrive exactly once. This level could be used, for example, with billing systems where duplicate or lost messages could lead to incorrect charges being applied.
- A small transport overhead and protocol exchanges minimized to reduce network traffic.
- A mechanism to notify interested parties when an abnormal disconnection occurs.
The diagram below illustrates the basic data flow with MQTT messaging.